🧬 How the Mediterranean Diet Rapidly Transforms Your Gut Microbiome
Our gut microbiome—home to trillions of bacteria, fungi, and even viruses—is profoundly shaped by what we eat. While the Mediterranean Diet is known for its long-term health benefits, compelling research shows that gut microbes respond to dietary changes in just 24–48 hours.
Let’s explore how the Mediterranean Diet reshapes the gut and what science says about how quickly our microbial communities react to dietary interventions.
🥗 The Mediterranean Diet: Microbiome Fuel
The Mediterranean diet (MedDiet) emphasizes:
✅ Fruits, vegetables, legumes, whole grains
✅ Olive oil and healthy fats
✅ Minimal red meat and processed foods
✅ Moderate consumption of fish and dairy
This high-fiber, anti-inflammatory diet creates an environment where beneficial gut bacteria flourish—and that change begins faster than most people think.
🚀 How Fast Does Diet Impact the Gut Microbiome?
In a groundbreaking study published in Nature by David et al. (2014), researchers found:
“Short-term consumption of diets composed entirely of animal or plant products alters microbial community structure and overwhelms inter-individual differences in microbial gene expression.”
🔍 Key Findings:
Changes within 24–48 hours of diet shift.
Animal-based diets increased bile-tolerant microbes like Bilophila and Bacteroides.
Plant-based diets enriched fiber-fermenting bacteria like Roseburia and Eubacterium.
Microbial gene activity began to mimic that of herbivorous or carnivorous animals.
Foodborne microbes from meals were detectable in the gut temporarily.
🌿 What Happens When You Switch to a Mediterranean Diet?
The Mediterranean Diet doesn’t just nourish you—it feeds your gut ecosystem. Here's how:
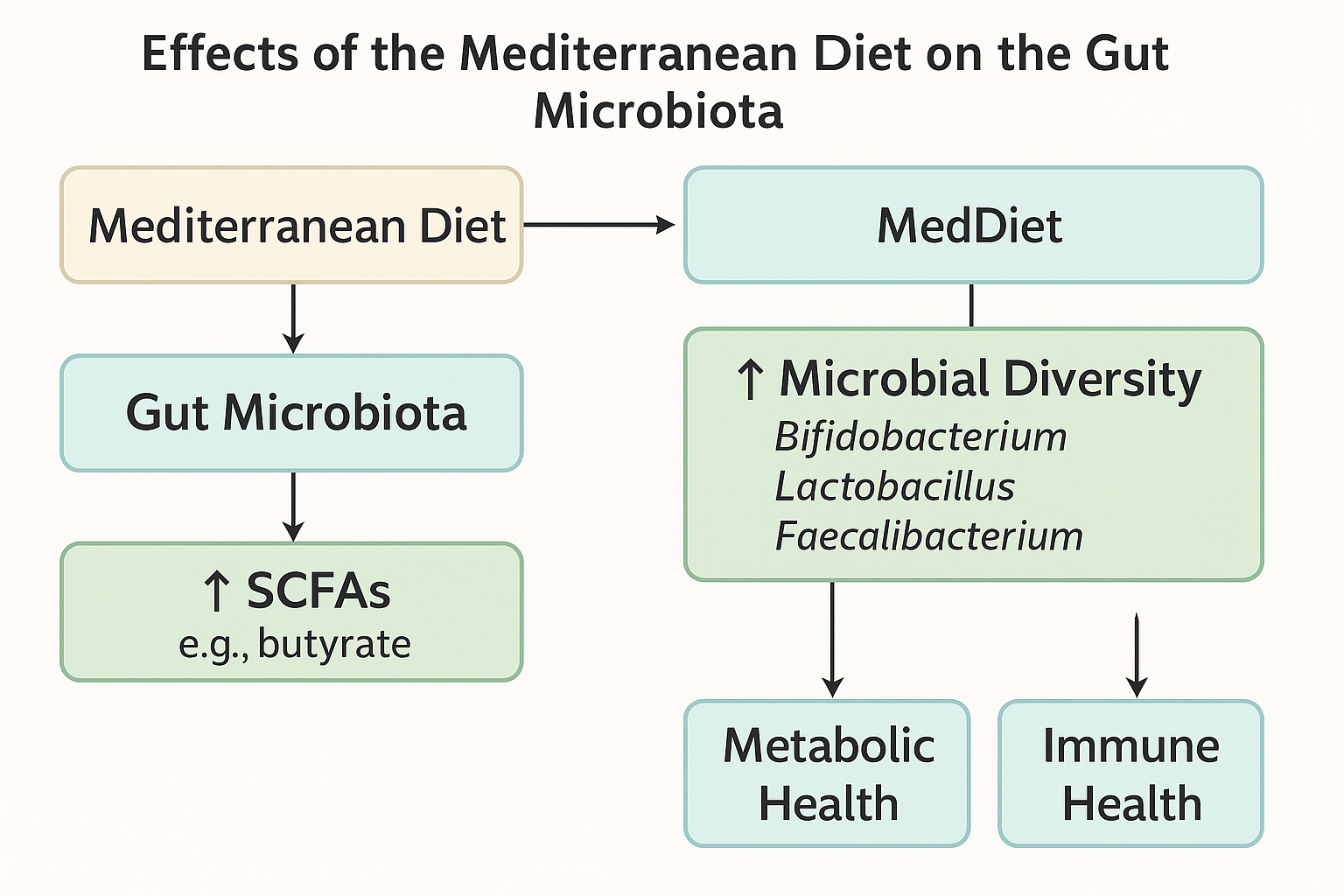
1. ↑ Microbial Diversity
Boosts bacteria like Bifidobacterium, Lactobacillus, and Faecalibacterium.
These microbes play key roles in digestion, immunity, and anti-inflammation.
2. ↑ SCFAs (Short-Chain Fatty Acids)
Especially butyrate, a microbial metabolite that:
Feeds gut lining cells
Regulates immune function
Reduces inflammation
3. ↓ Pathogenic Microbes
Unlike high-fat, animal-based diets that promote bile-tolerant pro-inflammatory bacteria (e.g., Bilophila wadsworthia), MedDiet keeps them in check.
🔄 Snapshot of Gut Response Timeline
Time After Diet ChangeGut Microbiota Impact24–48 hoursMicrobial gene expression shifts3–7 daysCommunity composition begins changing2–4 weeksNoticeable microbial diversity and SCFA increase3+ monthsStable microbiota remodeling, improved resilience
📊 Diagram: Effects of the Mediterranean Diet on Gut Microbiota
"This visual outlines how the Mediterranean Diet enhances gut microbial diversity, boosts SCFAs, and supports immune and metabolic health."
🧠 Final Thoughts
The gut microbiome is incredibly responsive to diet. Whether you're switching to plant-based eating or adopting a traditional Mediterranean pattern, changes start within days and compound over time. For those seeking a gut-friendly, sustainable approach to health, the Mediterranean Diet offers a scientifically supported, delicious path forward.